Nickel 28 Capital Corp.
Suite 5300, TD Bank Tower,
Box 48, 66 Wellington Street West, Toronto, ON M5K 1E6
info@nickel28.com
Nickel is not just for Electric Vehicles
Demand for nickel in electric batteries is driving the headlines, but use across heavy industry still dominates first use of nickel — and is expected to rise until at least 2040.
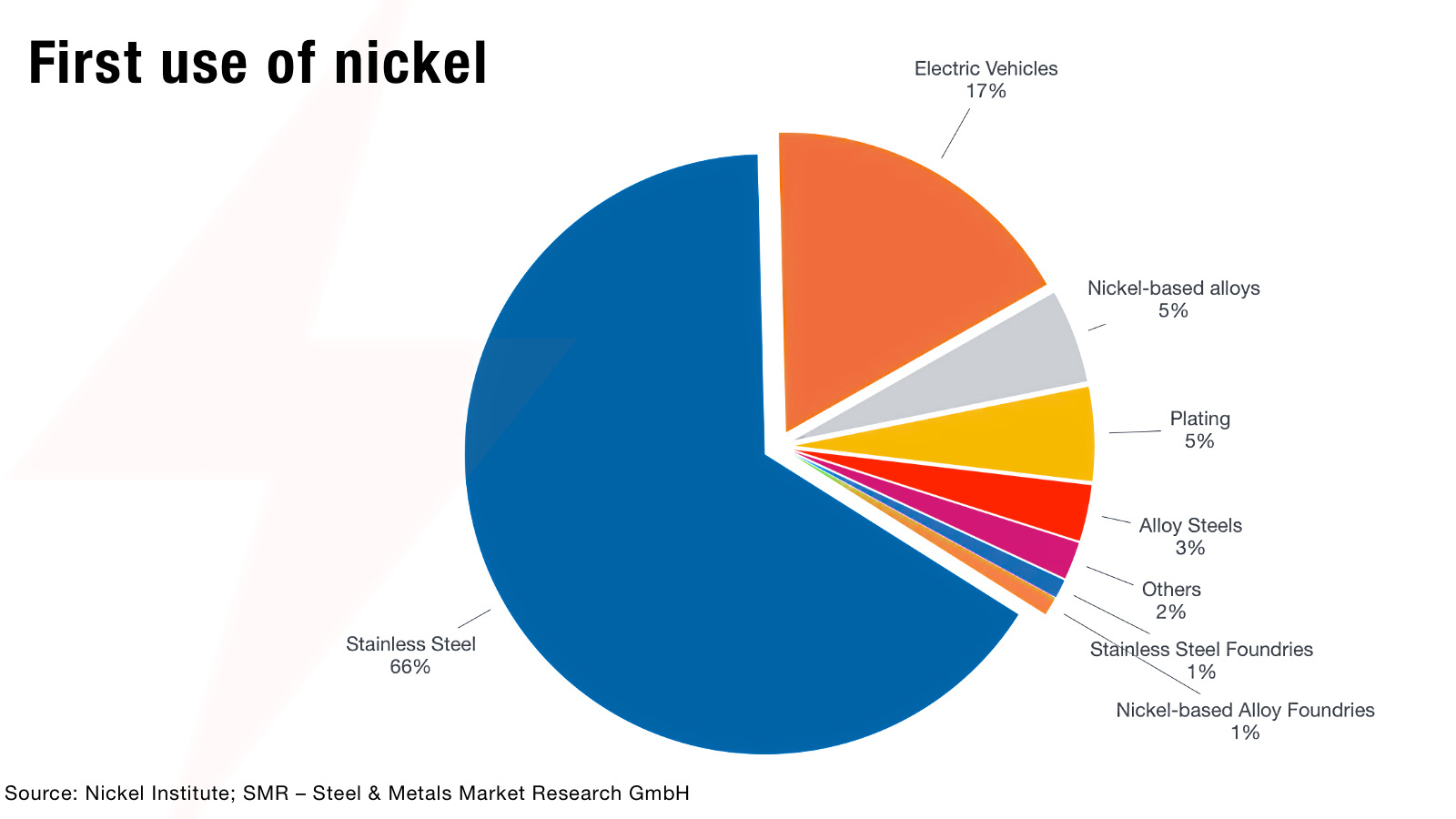
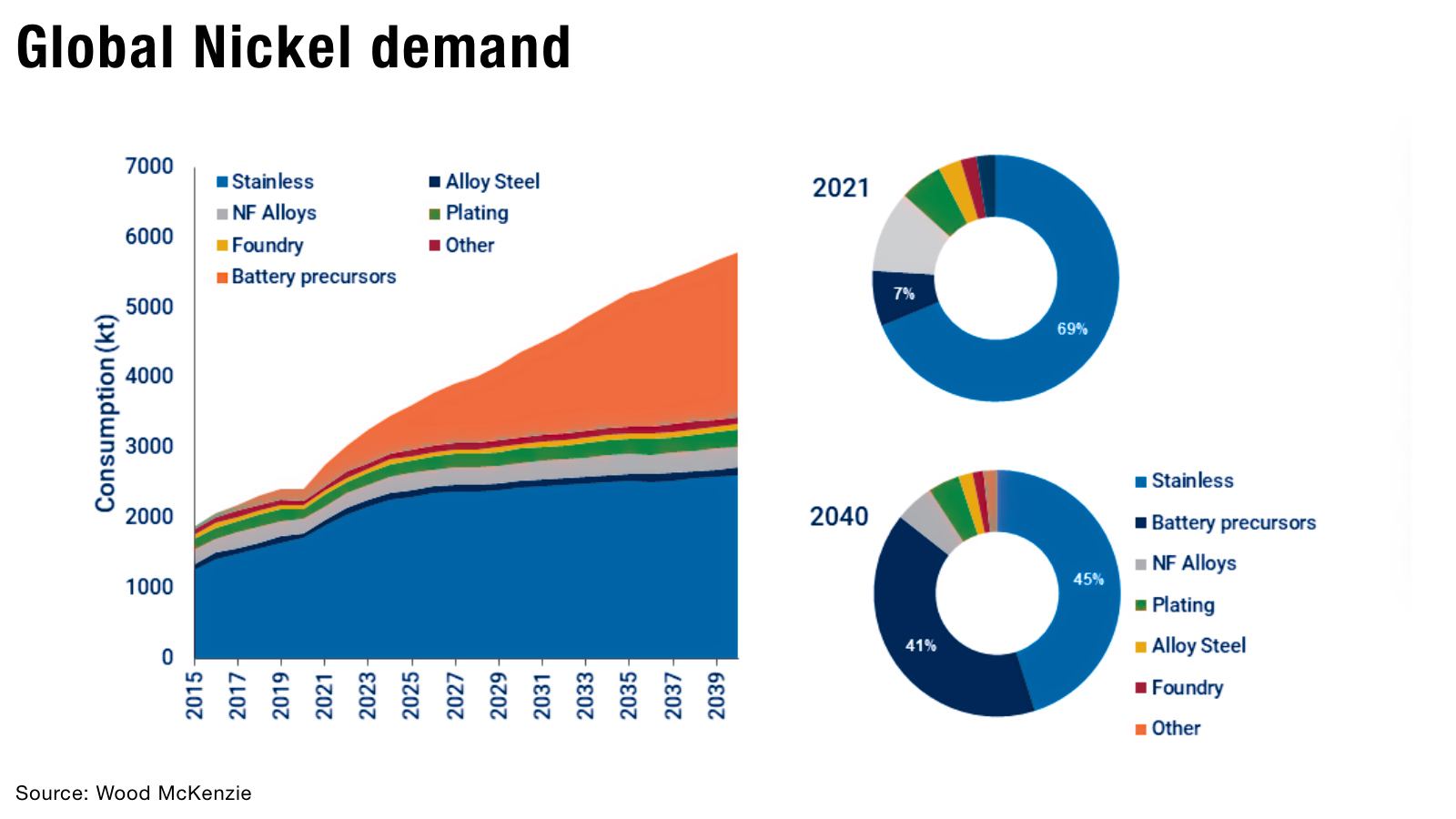
Demand for nickel is forecast to almost double due to demand for electric batteries, putting significant pressure on supply that is already tightening (as we highlighted in our previous blog post Nickel: short-term pain, long-term gain).
But the reason this new growth matters is because nickel’s critical role in traditional industrial applications remains so resilient. These applications include:
Nickel's role in heavy industry
1. Stainless steel production
Stainless steel is the largest consumer of nickel, accounting for over two-thirds of total nickel production.
Chromium gives the steel its "stainless" quality, but it is nickel that makes stainless steel such a versatile alloy for use across industry, including:
- enhancing resistance to corrosion
- easier to form and weld
- increased toughness
- ductile at low temperatures, and can be used for high temperature applications
- non-magnetic
Nickel is so important in stainless steel, that nickel-containing stainless steel grades make up 80% of stainless steel production across:
- construction: stainless steel is used in building frameworks, bridges, and other infrastructure due to its durability and resistance to corrosion
- automotive industry: traditional automotive manufacturing relies on stainless steel for exhaust systems, engine components and structural parts
- household appliances: from kitchen sinks to washing machines, stainless steel is a common material across household appliances due to its aesthetic appeal and longevity
2. Nickel based alloys
Nickel is also important in a variety of non-ferrous alloys, including copper and chromium, which can be used in specialized properties requiring specific properties, such as high-temperature strength and shape memory. For example,
- Monel: an alloy of nickel and copper, Monel is highly resistant to corrosion and is used in marine engineering, chemical processing, and aerospace applications
- Inconel: nickel and chromium, Inconel alloys are known for their high-temperature strength and oxidation resistance, making them ideal for gas turbines, jet engines, and other high-stress environments
- Nimonic: nickel-chromium alloys are used in the aerospace industry for turbine blades and other components subjected to extreme temperatures
3. Plating and coatings
Nickel plating is another significant application, providing both decorative and functional benefits. Nickel coatings are used to enhance the appearance, durability, and corrosion resistance of various products. Types of nickel plating include:
- Electroplated nickel: commonly used for decorative finishes on consumer goods, electroplated nickel provides a shiny, corrosion-resistant surface
- Electroless nickel coating: offers uniform thickness and is used in engineering applications where precision and wear resistance are critical
- Composite plating: combining nickel with other materials like silicon carbide, composite plating is used in high-wear applications such as automotive parts and industrial machinery
4. Alloy steels
Nickel is also used in the production of alloy steels, which are steels combined with other elements to improve their mechanical properties. Alloy steels containing nickel are used in:
- Oil and gas industry: drill pipes, valves, and other components in the oil and gas industry require high-strength materials that can withstand harsh environments
- Military: armor plating and other military equipment benefit from the toughness and strength provided by nickel-containing alloy steels
Emerging applications and future demand
As industries continue to innovate and seek more efficient materials, demand for nickel in a variety of sectors is expected to grow:
1. Renewable energy technologies
Nickel is crucial in the development of renewable energy technologies with the International Energy Agency (IEA) projecting, by weight, mineral demand in 2040 will be dominated by graphite, copper and nickel — which will increase 89-fold.
- Wind turbines: nickel alloys are used in the production of wind turbines, from gearboxes to ladders — and, note, a gearbox for an 8MW turbine can weigh 86 tons, with much of the steel in current gearboxes containing as much as 2% nickel for some components
- Solar panels: nickel is used in the production of certain types of solar cells, for example, providing ductility and hardness against wear and corrosion, as well as a silver-white finish
- Hydrogen: alkaline electrolysers are currently the most widely used in hydrogen power development, which require nickel in quantities of more than one tonne per MW
- Geothermal: corrosive compounds and gases at high temperatures in geothermal energy mean nickel-containing materials are essential to avoid corrosion. Of the total mineral demand from all low-carbon power sources in 2040, in a Sustainable Development Scenario, geothermal is forecast by the IEA to account for 80% of nickel demand
2. Other technology
- 3D printing: increasingly uses nickel alloys across aerospace, medicine, and other industries requiring intricate parts
- Marine scrubbers: nickel-alloys in scrubbers for marine engines used to help ships meet new environmental regulations
- Nanotechnology: combining nanoparticles with nickel alloys can enhance strength, wear resistance and high-temperature performance. And, in Metal Matrix Composites (MMCs), integrating nickel alloys with reinforcing elements like ceramic fibers can create composites with superior properties
- Surgical instruments: nickel-containing stainless steel is used in the production of surgical instruments due to its strength and ease of sterilization
- Medical implants: nickel-titanium alloys, known as Nitinol, are used in stents, guidewires, and other medical implants due to their shape-memory properties and biocompatibility
Conclusion
Nickel is not just for electric vehicles, with a wide variety of use cases across heavy industry, from renewable energy to medical equipment, electronics to military hardware.
Electric vehicles may have put nickel under the spotlight, but its role in heavy industry and other applications continues to dominate demand.
Forward-Looking Information: Some of the posted entries on the CEO Corner may contain forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements address future events and conditions which involve inherent risks and uncertainties. Actual results could differ materially from those expressed or implied by them. Examples of forward looking information and assumptions include future estimates of the worldwide supply and demand for nickel and other metals and the effect that these changes could have on the short term and long term price of nickel and other metals on the world markets, statements regarding the future operating or financial performance of Nickel 28 including the net present value, metal recoveries, capital costs, operating costs, production, rates of return and payback. Forward looking statements involve known and unknown risks and uncertainties which may not prove to be accurate. Such statements are qualified in their entirety by the inherent risks and uncertainties surrounding future expectations. Among those factors which could cause actual results to differ materially are the following: market conditions and other risk factors listed from time to time in our reports filed with Canadian securities regulators on SEDAR at www.sedar.com.
In some cases, forward-looking statements can be identified by terminology such as "may", "will", "should", "expect", "projects", "plans", "anticipates" and similar expressions. These statements represent management's expectations or beliefs concerning, among other things, future operations and various components thereof affecting the economic performance of Nickel 28. Undue reliance should not be placed on these forward-looking statements which are based upon management's assumptions and are subject to known and unknown risks and uncertainties, including the business risks discussed above, which may cause actual performance and financial results in future periods to differ materially from any projections of future performance or results expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements. Accordingly, readers are cautioned that events or circumstances could cause results to differ materially from those predicted.
Links: Some of the posted entries on the CEO Corner may include links to 3rd party websites. Nickel 28 has not reviewed all websites linked to or from this Site and is not responsible for the contents of any such websites. The inclusion of any link does not imply endorsement by Nickel 28 of the linked website or its content. Use of any such linked website is at the user's own risk.
For further information we refer you to our legal notice.

